Types of Security Controls
Compare and contrast various types of security controls.
— Dusty

What are Security Controls?
A security control is a measure or mechanism implemented to mitigate, manage, or eliminate security risks and threats to an organisation's assets, whether they are physical, digital, or of a different form.
There are many different risks and attack vectors to protect our assets from which means we must have just as many types of security controls to protect against them.
They fall into four main categories and six types of controls that we will learn today but first let us learn what are the "assets" we are protecting.
What are Assets?
Assets are anything of value. That's it.
That value can be monetary or of a different form. As long as it has a value to you, your organisation, your employees etc. It is an asset.
Therefore if an asset is anything of value and that value can be of multiple different forms then there are an infinite amount of possibilities as to what an asset can be but a few common examples would be;
- Data
- Computer Systems
- Physical Property
- Files
- Resources
- Employees
- Utilities (Yes, even your electricity and gas supply can be considered an asset)
Why protect these assets? Well, if these assets have a value to you, they will have even more value to an attacker who is targeting you, so they must be protected.
Security Control Categories
Now that we know what security controls and the assets they protect are, let's take a look at the four main categories of security controls.
- Technical Controls: These types of controls involve the implementation of technologies to protect and enforce the Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of our assets.
- Examples: Firewall rules, Encryption, AntiVirus Software, Operating System Controls etc.
- Managerial Controls: This pertains to the policies, procedures, strategies and other administrative methods devised to manage and oversee security design and implementation within an organisation .
- Examples: Regular Risk Assessments, Security Policy Documentation and Implementation, Standard Operating Procedures etc.
- Operational Controls: This refers to controls that are mostly implemented and carried out by people instead of systems to manage the operation of both digital and physical assets in a secure manner.
- Examples: Security Guards, Employee Awareness Programmes, Access Management Reviews, Log Reviews, Best practice etc.
- Physical Controls: Physical security controls are any physical implementation that limit physical access and risk to assets.
- Examples: Fences, Fire Extinguishers/Sprinklers, Locks, Bollards, Perimeter Lighting etc.
Security Control Types
- Preventive
Controls: These aim to stop a threat before it occurs, mainly by preventing physical or digital access.
- Examples: Firewalls, Door Locks and Encryption.
- Deterrent Controls: These aim to deter and discourage an attacker from attempting to intrude but does not directly prevent access like a Preventive Control.
- Examples: Warning Signs, Guard Dogs and Security Cameras.
- Detective
Controls: Designed to identify and detect security events that have already occured.
- Examples: Intrusion Detection Systems and Security Patrols.
- Corrective Controls: These aim to remediate the impacts of a security event once it is detected.
- Example: Backups to restore after a Ransomware attack.
- Compensating
Controls: These aim to mitigate any risks that cannot be remediated and must have an exception from the standards laid out in the security policy. These are usually temporary and shouldn't be a long term solution.
- Examples: Application Segmentation and Backup Generators.
- Directive Controls: These aim to guide and direct employees and others to comply with the security policies. These are a weaker form of control as it is ultimately up to the end subject to decide whether they will follow or not. However, if paired with other forms of controls that may enforce consequences of not following then these can become a much stronger type of control.
- Example: Acceptable Use Policy and Authorised Personnel Only warning signs.
While it's necessary to learn the definitions of all these categories and control types individually, it's important to know they are not mutually exclusive and to understand how they might fit together. Below is a table showing just one possible way that these Categories and Control Types may align.
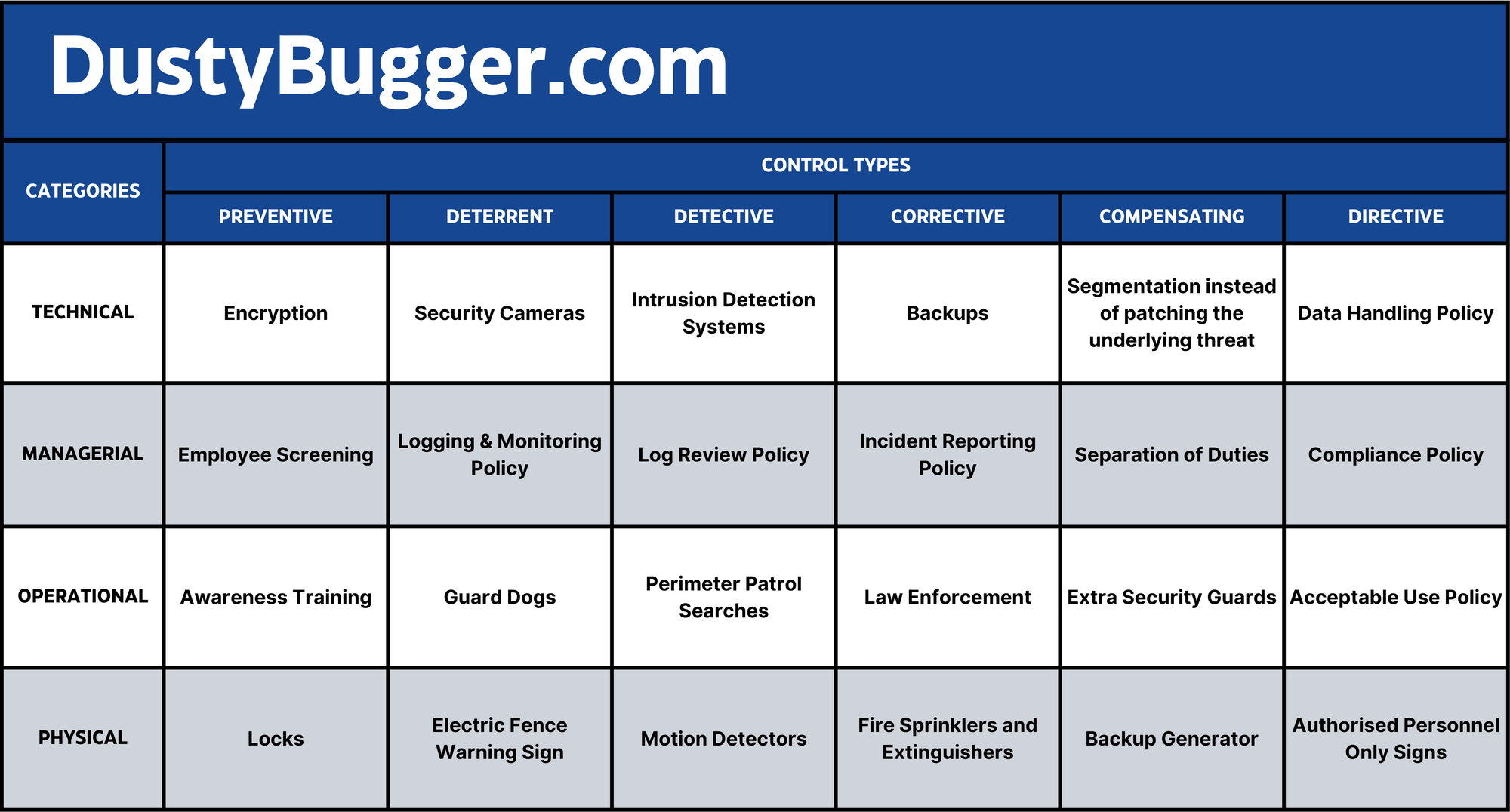
You should know that this can be quite vague and that the majority of security controls can fit into multiple different Types and Categories depending on the context of its use.
Also note that different organisations may combine certain categories or define them slightly differently.